How to Find the Right SaaS Packaging and Pricing?
- blogs
- 5 min read
By Keshav Vasudevan – Head of Product, Prepared
As a product manager, your pricing strategy is a critical factor in determining your revenue potential. Surprisingly, the average SaaS startup allocates a total of only six hours to develop, test, and refine its pricing strategy. This limited investment may stem from the overwhelming range of SaaS pricing models, strategies, and tactics available, making it challenging to know where to begin. This blog discusses the importance of pricing and different pricing strategies for SaaS products.
Key Takeaways:
- Pricing is a critical factor for product managers, directly impacting revenue potential.
- There are three major pricing strategies: cost-based pricing, competition-based pricing, and value-based pricing.
- Value-based pricing stands out for its customer-centric approach and effectiveness.
- Two key methodologies, the Van Westendorp Methodology, and value quantification, help businesses identify optimal pricing and quantify the value delivered to customers.
- A three-pronged approach to value-based pricing is followed to identify the value metric, identify the willingness to pay, and translate insights into packaging.
What exactly is Price?
Price isn’t just a number—it’s the essence of value. It reflects quality, utility, scarcity, brand reputation, and market demand, shaping our consumer perception. For businesses, pricing must align with this perceived value, presented effectively through packaging. Ultimately, price embodies the worth of a product or service, urging businesses to craft strategies that resonate with customers effectively.
Why Should You Care about Pricing as a Product Manager?
In product management, pricing often takes a backseat to tasks like backlog management and roadmap planning. However, understanding the significance of pricing is crucial for every product manager.
As a product manager, your role goes beyond product development; you serve as the bridge between market needs and company offerings. Pricing plays a pivotal role in delivering value to customers and shaping their perception of your product or service.
Imagine this scenario: You’ve meticulously designed an exceptional product, but if its pricing doesn’t hit the mark—either too high or too low—it could create a failed product. Pricing directly impacts critical business metrics such as revenue, margin, customer lifetime value, and churn, acting as the glue that binds your marketing, sales, and product efforts together.
Market data suggests that pricing efficiency can have twice the impact of improving retention and four times the efficiency of boosting acquisition efforts.
Founders struggling to raise capital for startups often attribute their challenges to late monetization or choosing the wrong business model, highlighting the significance of pricing decisions.
Zoom’s user-based pricing model serves as a great case of clarity, transparency, and alignment with different customer segments, proving the power of effective pricing strategies.
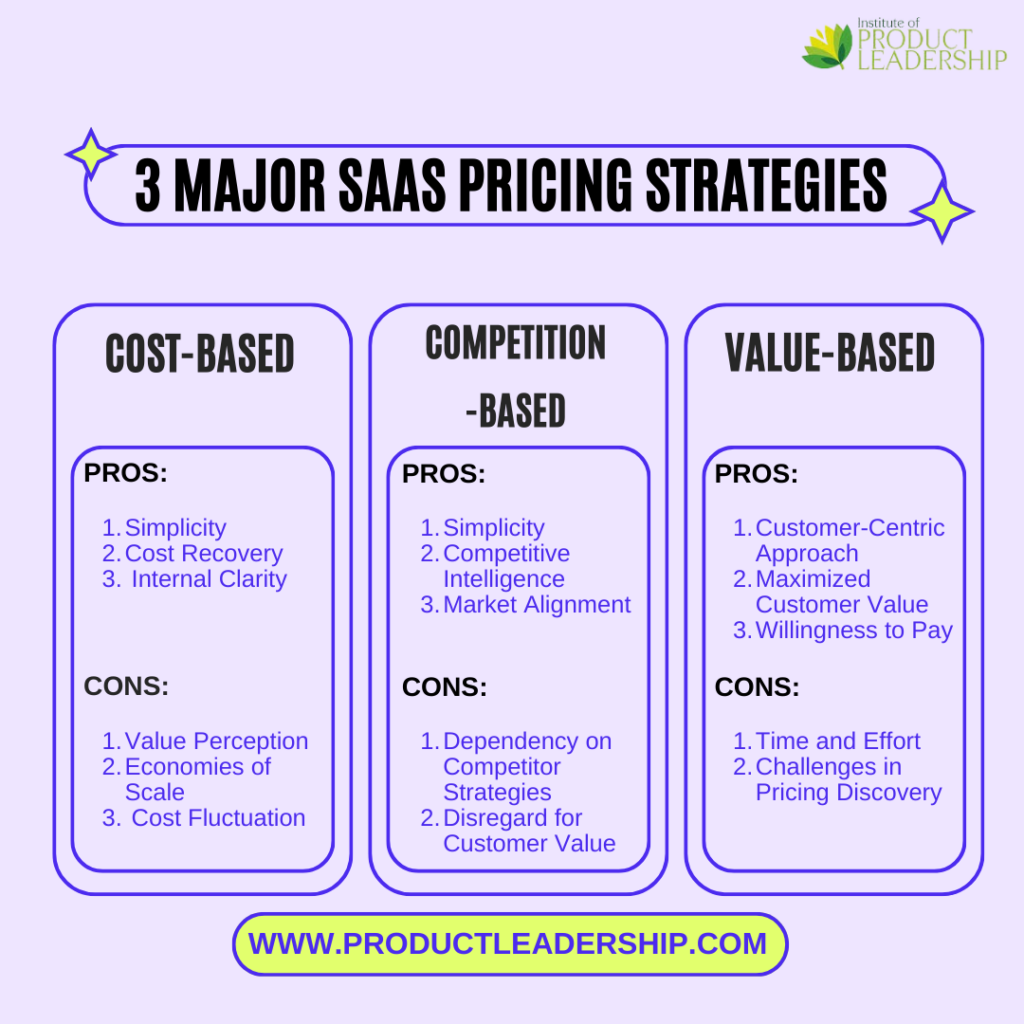
What are the 3 Major SaaS Pricing Strategies?
The most commonly used pricing strategies used in SaaS product development are:
1. Cost-Based Pricing
Cost-based pricing is a straightforward method where the price of a SaaS product is determined by adding a markup to the total costs involved in producing or delivering it.
Pros of Cost-Based Pricing
- Simplicity: Cost-based pricing is easy to implement and understand, making it accessible to businesses of all sizes.
- Cost Recovery: By factoring in all expenses, businesses ensure that their costs are covered, providing a sense of financial security.
- Internal Clarity: The pricing rationale is transparent and easy to communicate internally, facilitating decision-making and stakeholder alignment.
Cons of Cost-Based Pricing
- Value Perception: Cost-based pricing may undervalue the SaaS product, leading to missed opportunities for capturing the true value offered to customers.
- Economies of Scale: As businesses grow and achieve economies of scale, the cost per unit may decrease, but cost-based pricing may fail to reflect the increased value generated.
- Cost Fluctuations: In SaaS businesses, costs fluctuate frequently due to factors like technology updates, compliance requirements, and market trends, posing challenges in maintaining pricing consistency.
How Cost Fluctuation Impacts Price
Cost fluctuations can have a significant impact on your pricing decisions and ultimately affect your bottom line.
Cost fluctuations occur when the expenses associated with producing or delivering the SaaS product vary over time. These fluctuations can be attributed to various factors such as changes in raw material prices, labor costs, technology upgrades, or market dynamics.
In a scenario where costs fluctuate but prices remain constant over a period, the impact on profit margins becomes evident. While the revenue generated may remain stable, fluctuating costs can erode profit margins, affecting the overall profitability of the business.
Certain industries, such as platform as a service (PaaS) businesses or those reliant on third-party APIs, may necessitate a cost-based pricing approach. For example, in PaaS models where the cost of maintaining and delivering services is exponential, businesses may adopt a pass-through model, where additional costs incurred are passed on to customers.
2. Competition-Based Pricing
Pricing based on competition involves analyzing the pricing strategies of key competitors in the market and aligning your prices accordingly. This approach involves conducting comparative analyses to gauge where your product’s pricing stands relative to competitors’ offerings.
Pros of Competition-Based Pricing
- Simplicity: Implementing a SaaS pricing strategy based on competition is straightforward and swift. By leveraging existing competitive data, businesses can swiftly position their products within the market.
- Competitive Intelligence: Engaging in competitive pricing analysis offers valuable insights into market trends, competitor positioning, and customer expectations. This data can inform strategic decision-making and enhance overall competitiveness.
- Market Alignment: Pricing your product in line with competitors’ offerings helps ensure that your prices are within the expected range for consumers. This alignment reduces the risk of price perception issues and enhances market acceptance.
Cons of Competition-Based Pricing
- Dependency on Competitor Strategies: Relying solely on competitor pricing strategies can limit your business’s ability to differentiate and innovate. It may lead to missed opportunities to capture additional value or address unique customer needs.
- Disregard for Customer Value: Focusing excessively on competitor pricing overlooks the importance of customer-centric pricing. Businesses may fail to adequately consider the unique value proposition they offer and the benefits perceived by customers.
While pricing based on competition may be suitable for certain industries, it is essential to approach it as one aspect of a comprehensive SaaS pricing strategy. Businesses should conduct thorough market research, consider customer value, and strive for differentiation to maximize pricing effectiveness.
3. Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing revolves around determining the worth of your offering to your target market and setting prices accordingly. Instead of merely considering production costs or competitor prices, this approach prioritizes the perceived value and benefits received by customers.
Pros of Value-Based Pricing
- Customer-Centric Approach: By aligning prices with the value delivered to customers, product managers can demonstrate a deep understanding of their needs and preferences. This customer-centric focus fosters stronger relationships and enhances brand loyalty.
- Maximized Customer Value: Value-based pricing allows businesses to optimize the value proposition of their offerings, thereby maximizing customer satisfaction and loyalty. By delivering tangible benefits that resonate with customers, businesses can differentiate themselves in the market.
- Willingness to Pay: This approach accounts for the willingness of customers to pay for the unique benefits and outcomes offered by the product or service. By understanding customers’ perceived value, businesses can capture a fair share of the market and maximize revenue.
Cons of Value-Based Pricing
- Time and Effort: Implementing value-based pricing requires thorough market research, customer discovery, and pricing discussions. It demands time and effort to accurately assess customer needs and quantify the value proposition.
- Challenges in Pricing Discovery: Engaging in pricing discussions with customers can be daunting, as it involves probing into their perception of value and willingness to pay. Overcoming these challenges requires proactive communication and a deep understanding of customer needs.
Three-Pronged Approach to Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing stands out for its customer-centricity and effectiveness. However, implementing this approach requires a structured methodology.
Let’s explore a three-pronged approach to value-based pricing and delve into practical insights into its execution.
1. Identify the Value Metric
The first step in value-based pricing is to identify the core pricing metric or value metric. This metric serves as the foundation for determining the value delivered to customers. Whether it’s per user, per transaction, per widget, or per group, the value metric should align closely with the tangible benefits offered by the product or service. For instance, AWS bases its pricing on metrics like per compute, reflecting the usage-based nature of its services.
2. Quantify Willingness to Pay
Once the value metric is established, the next step is to quantify customers’ willingness to pay. This involves conducting thorough market research, customer surveys, and pricing discussions to gauge how much customers are willing to invest in the product or service. Understanding customers’ perceived value and their readiness to pay for the benefits offered is essential for setting optimal prices.
3. Craft Packaging Based on Data
Armed with insights from the value metric and willingness to pay analysis, the final step is to craft packaging that aligns with customer expectations and market dynamics. This involves bundling offerings, defining pricing tiers, and designing pricing plans that resonate with different customer segments.
A critical aspect of implementing value-based pricing is establishing a pricing committee within the organization. This committee, comprising representatives from product management, sales, marketing, and executive leadership, is tasked with regularly reviewing and refining the pricing strategy. By incorporating feedback from market data, CRM insights, and sales team inputs, the pricing committee ensures that pricing decisions are informed and aligned with business objectives.
How to Identify SaaS Value and Pricing Metrics?
In pricing strategies, selecting the right metric is crucial. It directly shapes customer perceptions of your product’s value. It determines what aspect of your offering drives pricing, like users or transactions. Spotify and Netflix, for example, base pricing on user count, reflecting scalability.
An optimized value metric maximizes product value and minimizes churn. It should be simple, align with customer needs, and ensure transparent pricing. Empathizing with customer budgets enhances satisfaction and clarity in pricing.
There are two main methods of identifying the value metric: Discovery framework and Customer engagement.
1. Discovery Framework
The Discovery Framework involves a systematic exploration of where the true value of your product lies. By identifying the core features and outcomes that resonate with your target audience, you can formulate a thesis on potential value metrics. This process requires continuous feedback and interaction with customers to gain insights into their preferences and priorities.
2. Customer Engagement
Engaging with customers directly is paramount in validating your value metric hypotheses. Conducting face-to-face discussions or surveys allows you to present different pricing packages and gauge customer preferences effectively. Utilizing techniques like card sorting exercises enables customers to prioritize features and outcomes, providing invaluable insights into their perceived value. By quantifying relative preference metrics, you can visualize customer preferences and tailor your SaaS pricing strategy accordingly.
How do you identify customer willingness to pay?
User-based pricing customizes plans based on individual user needs and usage patterns, offering flexibility and alignment with the value delivered. It relies on understanding customer behavior and willingness to pay, driven by data insights from customer preferences, market trends, and competition
Two SaaS pricing frameworks are used- Van Westerndorp methodology and value quantification.
1. Van Westendorp Methodology
Named after economist Peter Van Westendorp, the Van Westendorp methodology serves as a compass for navigating price sensitivity. At its core, this approach seeks to identify acceptable price ranges and gauge customer perceptions of value. By posing targeted questions to customers, businesses can uncover crucial insights into pricing dynamics:
- Threshold of Expensiveness: At what price would the product be deemed too expensive to consider purchasing?
- Threshold of Cheapness: At what price would the product be perceived as low-quality or too cheap?
- Optimal Price Point: What price represents a bargain for value, striking the perfect balance between affordability and perceived quality?
Through rigorous analysis of customer responses, businesses can pinpoint the optimal price range that maximizes revenue while remaining competitive in the market. The Van Westendorp methodology offers a nuanced understanding of customer willingness to pay, guiding businesses toward informed pricing decisions.
2. Value Quantification Methodology
While the Van Westendorp methodology illuminates price sensitivity, value quantification dives into the tangible benefits delivered by a product. This approach focuses on quantifying the value proposition in terms of time savings, risk reduction, revenue generation, and cost-effectiveness:
- Time and Effort Savings: How much time and effort does the product save for users, and what is the monetary value of this efficiency gain?
- Risk Reduction: What is the monetary value of mitigating risks or preventing potential losses for customers?
- Revenue Generation: How does the product contribute to revenue generation or business growth, and what is the financial impact?
- Cost-Effectiveness: In what ways does the product replace or streamline existing processes, resulting in cost savings or operational efficiencies?
By quantifying the value delivered across these dimensions, businesses can establish a compelling rationale for their pricing strategy. Value quantification provides a concrete framework for articulating the ROI of the product and justifying its price point to customers.
Combination of Van Westendorp and Value Quantification Methodology
The synergy between the Van Westendorp methodology and value quantification is key to crafting a robust pricing strategy. By combining insights from both approaches, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of customer preferences, perceptions, and value drivers. This integrated approach empowers businesses to:
- Identify optimal price ranges that align with customer expectations and market dynamics.
- Quantify the tangible benefits and ROI offered by the product, enhancing its value proposition.
- Tailor pricing strategies to different customer segments based on their unique needs and preferences.
- Continuously refine pricing strategies based on real-time feedback and market insights
Translating Insights into Packaging
For small and medium enterprises (SMEs), understanding their unique needs and preferences is essential when it comes to packaging products and setting prices. Let us discuss the key SaaS packaging and pricing features that matter most to SMEs, their price sensitivity, and how businesses can craft tailored packages to cater to this segment effectively.
On average, SMEs prioritize certain features over others when considering a product or service. They value solutions that offer efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. Additionally, SMEs tend to be more price-sensitive compared to larger enterprises. However, their willingness to pay may vary depending on the perceived value of the offering.
Methods of Creating Tailored Packages
Based on these insights, businesses can design packages specifically tailored to the needs and preferences of SMEs. By offering a range of features that align with their priorities and price sensitivity, businesses can enhance the appeal of their products or services to this segment. Here’s how:
1. Feature Alignment: Identify the key features that resonate most with SMEs. Focus on functionalities that streamline processes, reduce costs, and drive growth for their businesses.
2. Price Optimization: Set prices that reflect the value delivered while remaining competitive in the market. Understand the price sensitivity of SMEs and offer flexible pricing options that accommodate their budgets.
3. Clear Value Proposition: Communicate the value proposition clearly and succinctly. Highlight how the product or service addresses the specific needs and challenges faced by SMEs, making it a compelling choice for their business.
4. Segmentation Strategy: Recognize that SMEs may vary in their requirements and preferences. Segment the market based on factors such as industry, company size, and growth stage, and tailor packages accordingly.
Operational Implementation
4 Steps to operationalize pricing and packaging strategies effectively:
1. Establish a pricing committee comprising key stakeholders from product, finance, sales, and marketing departments.
2. Regularly review pricing and packaging based on data collected from sales, marketing, customer success, and renewals.
3. Utilize customer feedback and data insights to iterate on pricing strategies and optimize package offerings.
4. Conduct in-depth analysis, including customer interviews and competitive benchmarking, to inform pricing decisions and address potential cannibalization concerns.
Hence, mastering pricing is a crucial skill for product managers. By understanding the significance of pricing and implementing effective strategies, you can unlock revenue potential, drive customer satisfaction, and propel your business toward sustainable growth. Remember, pricing isn’t static—it’s a journey of continuous refinement and adaptation.
About the Author
Keshav Vasudevan – Head of Product, Prepared
Frequently Asked Questions
A pricing strategy includes the methodology employed by businesses to set optimal prices for their products and services. This involves thorough market analysis, assessing customer demand and preferences, considering production expenses, and establishing competitive pricing structures aimed at maximizing profitability.
The three main approaches to pricing strategy are cost-based pricing, competition-based pricing, and value-based pricing.
- Simplicity: Cost-based pricing is easy to implement and understand, making it accessible to businesses of all sizes.
- Cost Recovery: By factoring in all expenses, businesses ensure that their costs are covered, providing a sense of financial security.
- Internal Clarity: The pricing rationale is transparent and easy to communicate internally, facilitating decision-making and stakeholder alignment.
Value-based pricing revolves around determining the worth of your offering to your target market and setting prices accordingly. Instead of merely considering production costs or competitor prices, this approach prioritizes the perceived value and benefits received by customers.
Named after economist Peter Van Westendorp, the Van Westendorp methodology serves as a compass for navigating price sensitivity. At its core, this approach seeks to identify acceptable price ranges and gauge customer perceptions of value. By posing targeted questions to customers, businesses can uncover crucial insights into pricing dynamics.